Description
Stainless Steel Forge Fitting Supplier in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Philippines, Indonesia
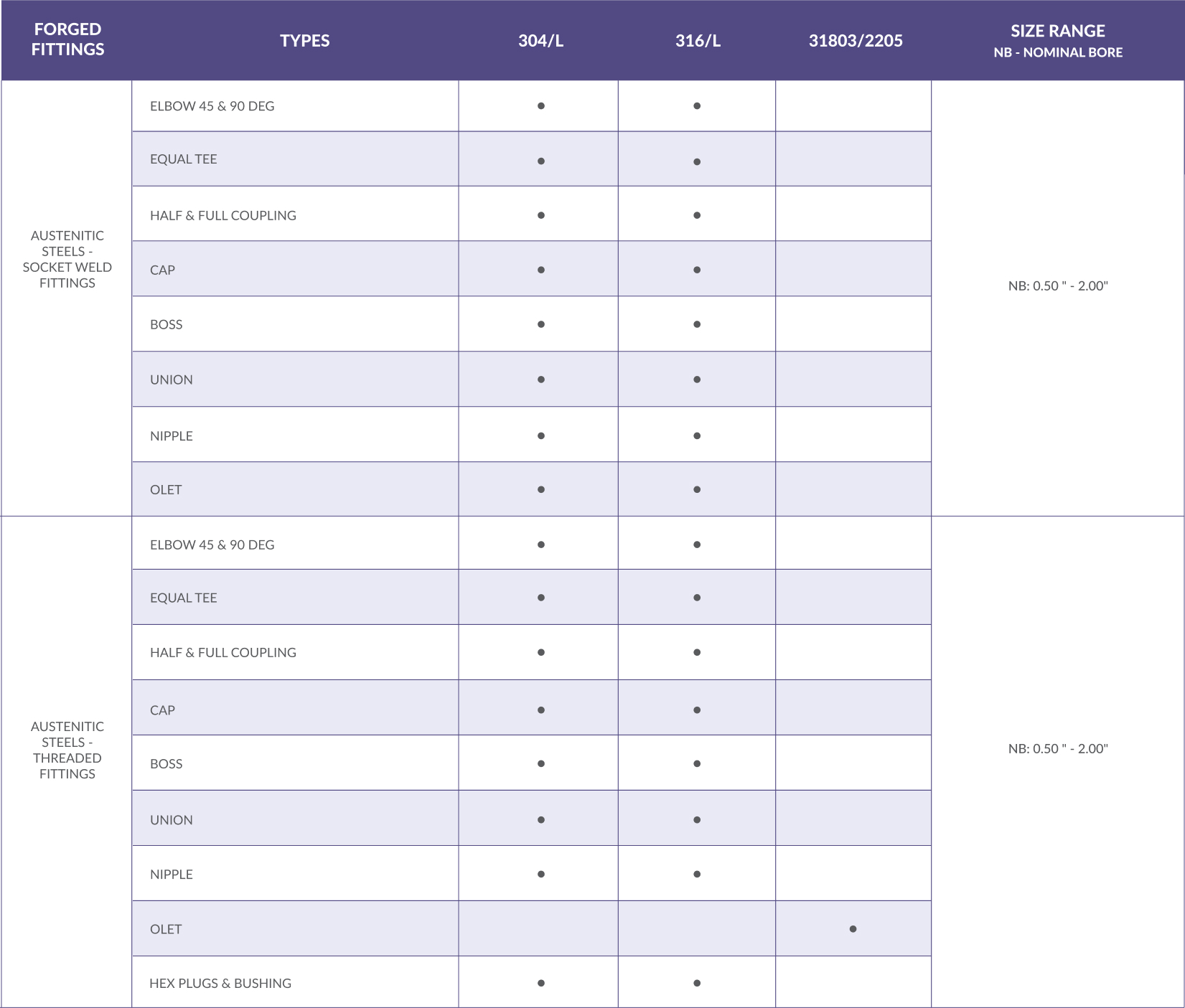
Forged Fittings
WHAT ARE FORGED FITTINGS
Forged fittings are formed via forging and machining from solid blocks of steel, stainless steel in our case to meet the final required shape set within the tolerances of the applicable specifications. These are split into two categories of forged fittings, namely Socket Weld Fittings and Threaded Fittings. These are further categorized in ratings of 3000#/6000#/9000#, the higher the class rating, the higher the pressure and temperature a fitting would be able to withstand.
Socket Weld Fittings are connected to pipes by fillet welds. It is typically used for when a strong and long-lasting connection is required. These are very reliable but also very time consuming due to welding of a small part.
Threaded fittings are screwed on fittings. It is typically used for less critical piping systems such as water distribution or for low pressure installations that are not subject to vibrations, elongations and bending forces. There are two types of common threading that one would find if they purchase threaded fittings and they are:
- BSP – BSP refers to British Standard Pipe and can be further divided into BSPT (Tapered) and BSPP (Parallel) as one of the few variations
- NPT – NPT refers to National Pipe Tapered.
Both these socket weld and threaded fittings are further categorized in ratings of 3000#/6000#/9000#, the higher the class rating, the higher the pressure and temperature a fitting would be able to withstand.
FORGED VS BUTTWELD FITTINGS
Forged fittings are typically used for piping systems that are smaller in nature as their manufacturing process does not allow for creation of larger fittings. Larger sized fittings are usually made via casting for buttweld fittings.
Forged fittings provides a higher tensile and fatigue strength as compared to buttweld fittings due to their superior casting process. This is not to say that forged fittings are superior but both types have their advantages. Casting provides one with a larger range of choices, as the tools used for casting are much cheaper and readily available.
In terms of application, the two types of forged fittings are in socket weld and threaded type. Socket weld fittings are connect to the pipes via fillet welds. Whereas threaded fittings are screwed onto the fitting itself. For buttweld fittings, these are connected via V weld (Buttweld)
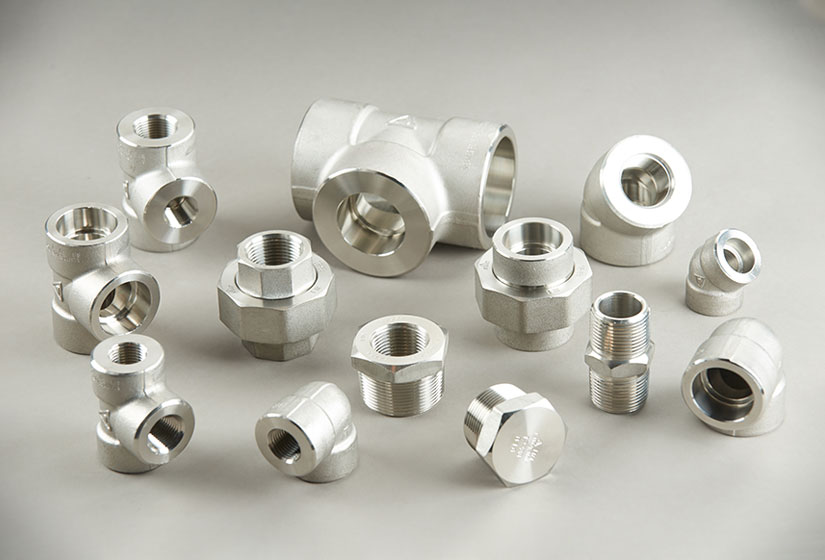

AVAILABLE TYPES
QUALITY ASSURANCE

FORGED TEE (EQUAL & REDUCING)
Forged tees are used to branch out a pipe at 90 degrees. These tees are either available in equal or reducing types. Forged tees are manufactured to ASME B16.11 and are available in either socket weld or threaded connections (NPT or BSP). The dimensions of forged tees are covered by the MSS SP 75 and the ASME B16.11 specifications.

FORGE COUPLING (HALF, FULL & REDUCING)
Forged Couplings are forged fittings manufactured in accordance with ASME B16.11 and are used to join pipes.
Full Couplings are used for connecting small bore pipes. It is used for connection between a pipe to pipe or pipe to swage or nipple. It can be threaded or socket ends types.
Half Couplings are used for small bore branching from a vessel or large bore pipe. It can be threaded or socket type. It has a socket or thread end on only one side.
Reducing couplings are used to connect pipes of dissimilar diameters. A reducing coupling has two different sizes of threads on each side. Reducing couplings are typically used where small process feeder lines are joined into large supply circuits or where small diameter fittings are installed.

OLETS
Olet fittings are used to create a branch connection between the Run Pipe (header) to the branch pipe, an Outlet. Here at HH stainless, we commonly keep the following:
Weldolets are the mostly commonly used among all olets fittings, they are well suited for high pressure applications. Weldolets are used to create a 90-degrees pipe branch. The shape of the Weldolet ensures little stress concentration on the branched pipe, providing an integral reinforcement.
Sockolets are similar to weldolets except that the branch pipe end will have a socket weld end. Sockolets are used to create a 90-degrees pipe branch and are typically used in lower pressure pipe lines in smaller diameters.
Threadolets serve a similar purpose to both the olets introduced above in which its purpose is to create a 90-degrees pipe branch. The main difference is that it has a female threaded end. The threadolet end is generally a NPT type.
Other types of olets include sweepolet / latrolet / elbolet / nipolet.

NIPPLE
A nipple is commonly fabricated from a short piece of pipe to be used as a fitting to connect between two pipes or fittings. Here at HH stainless, we commonly keep the following:
Barrel Nipples have both ends being NPT threaded. These are some of the most common types of pipe nipples due to their inherent strength and easy to remove design
Hex Nipples are similar to Barrel Nipples except that it has a hexagonal bolt shaped nut in the center. This allows for easy torquing, tightening or loosening using a wrench.
T.O.E Pipe Nipples stands for Threaded-One-End. These are usually not used to link any pipes together but are commonly used as legs for oil tanks.

WELDING BOSS
Welding bosses serves a similar purpose to Olets whereby it is used as a branch connection between the run pipe (header) or a nozzle connection on the equipment. It is available in either socket weld or threaded end.
A branch pipe is joined by socket welding or threaded connection of the boss. The boss is then welded onto the external surface of pipe header. Compared to a half coupling, the other end is bevelled at an angle